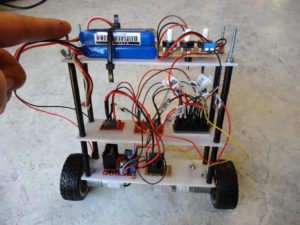
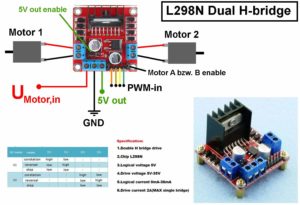
Ein Balancierrobotor ist quasi ein Segway in klein. Er lässt sich recht einfach mit dem Arduino umsetzen. Der aktuelle Winkel wird mit dem MPU6050 ermittelt und die Motoren werden mit dem Vollbrückenmodul LM298 angesteuert. Auf ebay bekommt man komplette Sets oder auch nur die Motor-Getriebe-Räder-Einheit. Ich verwende 12V Motoren mit 122 rpm.






Arduino-Code:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 230 231 232 233 234 235 236 237 238 239 240 241 242 243 244 245 246 247 248 249 250 251 252 253 254 255 256 257 258 259 260 261 262 263 264 265 266 267 268 269 270 271 272 273 274 275 276 277 278 279 280 281 282 283 284 285 286 287 288 289 290 291 292 293 294 295 296 297 298 299 300 301 302 303 304 305 306 307 308 309 310 311 312 313 314 315 316 317 318 319 320 321 |
#include <PID_v1.h> #include <LMotorController.h> #include "I2Cdev.h" #include "MPU6050_6Axis_MotionApps20.h" #if I2CDEV_IMPLEMENTATION == I2CDEV_ARDUINO_WIRE #include "Wire.h" #endif #define LOG_INPUT 0 #define MANUAL_TUNING 0 //MANUAL_TUNING must be 1 #define LOG_PID_CONSTANTS 0 #define MOVE_BACK_FORTH 0 #define MIN_ABS_SPEED 30 //MPU MPU6050 mpu; // MPU control/status vars bool dmpReady = false; // set true if DMP init was successful uint8_t mpuIntStatus; // holds actual interrupt status byte from MPU uint8_t devStatus; // return status after each device operation (0 = success, !0 = error) uint16_t packetSize; // expected DMP packet size (default is 42 bytes) uint16_t fifoCount; // count of all bytes currently in FIFO uint8_t fifoBuffer[64]; // FIFO storage buffer // orientation/motion vars Quaternion q; // [w, x, y, z] quaternion container VectorFloat gravity; // [x, y, z] gravity vector float ypr[3]; // [yaw, pitch, roll] yaw/pitch/roll container and gravity vector //PID #if MANUAL_TUNING double kp , ki, kd; double prevKp, prevKi, prevKd; #endif double originalSetpoint = 179.29; double setpoint = originalSetpoint; double movingAngleOffset = 0.3; double input, output; int moveState=0; //0 = balance; 1 = back; 2 = forth #if MANUAL_TUNING PID pid(&input, &output, &setpoint, 0, 0, 0, DIRECT); #else PID pid(&input, &output, &setpoint, 70, 270, 1.9, DIRECT); #endif //MOTOR CONTROLLER int ENA = 3; int IN1 = 5; int IN2 = 6; int IN3 = 9; int IN4 = 10; int ENB = 11; LMotorController motorController(ENA, IN1, IN2, ENB, IN3, IN4, 0.7, 0.7); // letzten beiden Zahlen = Korrekturfaktoren für linken/rechten Motor! //timers long time1Hz = 0; long time5Hz = 0; volatile bool mpuInterrupt = false; // indicates whether MPU interrupt pin has gone high void dmpDataReady() { mpuInterrupt = true; } // ******************************************************************** // **************************** SETUP ********************************* // ******************************************************************** void setup() { // join I2C bus (I2Cdev library doesn't do this automatically) #if I2CDEV_IMPLEMENTATION == I2CDEV_ARDUINO_WIRE Wire.begin(); TWBR = 24; // 400kHz I2C clock (200kHz if CPU is 8MHz) #elif I2CDEV_IMPLEMENTATION == I2CDEV_BUILTIN_FASTWIRE Fastwire::setup(400, true); #endif // initialize serial communication // (115200 chosen because it is required for Teapot Demo output, but it's // really up to you depending on your project) Serial.begin(115200); while (!Serial); // wait for Leonardo enumeration, others continue immediately // initialize device Serial.println(F("Initializing I2C devices...")); mpu.initialize(); // verify connection Serial.println(F("Testing device connections...")); Serial.println(mpu.testConnection() ? F("MPU6050 connection successful") : F("MPU6050 connection failed")); // load and configure the DMP Serial.println(F("Initializing DMP...")); devStatus = mpu.dmpInitialize(); // supply your own gyro offsets here, scaled for min sensitivity mpu.setXGyroOffset(220); mpu.setYGyroOffset(76); mpu.setZGyroOffset(-85); mpu.setZAccelOffset(-100); // 1688 factory default for my test chip // make sure it worked (returns 0 if so) if (devStatus == 0) { // turn on the DMP, now that it's ready Serial.println(F("Enabling DMP...")); mpu.setDMPEnabled(true); // enable Arduino interrupt detection Serial.println(F("Enabling interrupt detection (Arduino external interrupt 0)...")); attachInterrupt(0, dmpDataReady, RISING); mpuIntStatus = mpu.getIntStatus(); // set our DMP Ready flag so the main loop() function knows it's okay to use it Serial.println(F("DMP ready! Waiting for first interrupt...")); dmpReady = true; // get expected DMP packet size for later comparison packetSize = mpu.dmpGetFIFOPacketSize(); //setup PID pid.SetMode(AUTOMATIC); pid.SetSampleTime(10); pid.SetOutputLimits(-255, 255); } else { // ERROR! // 1 = initial memory load failed // 2 = DMP configuration updates failed // (if it's going to break, usually the code will be 1) Serial.print(F("DMP Initialization failed (code ")); Serial.print(devStatus); Serial.println(F(")")); } } // **************************************************************************** // **************************** HAUPTSCHLEIFE ********************************* // **************************************************************************** void loop() { // if programming failed, don't try to do anything if (!dmpReady) return; // wait for MPU interrupt or extra packet(s) available while (!mpuInterrupt && fifoCount < packetSize) { //no mpu data - performing PID calculations and output to motors pid.Compute(); motorController.move(output, MIN_ABS_SPEED); unsigned long currentMillis = millis(); if (currentMillis - time1Hz >= 1000) { loopAt1Hz(); time1Hz = currentMillis; } if (currentMillis - time5Hz >= 5000) { loopAt5Hz(); time5Hz = currentMillis; } } // reset interrupt flag and get INT_STATUS byte mpuInterrupt = false; mpuIntStatus = mpu.getIntStatus(); // get current FIFO count fifoCount = mpu.getFIFOCount(); // check for overflow (this should never happen unless our code is too inefficient) if ((mpuIntStatus & 0x10) || fifoCount == 1024) { // reset so we can continue cleanly mpu.resetFIFO(); Serial.println(F("FIFO overflow!")); // otherwise, check for DMP data ready interrupt (this should happen frequently) } else if (mpuIntStatus & 0x02) { // wait for correct available data length, should be a VERY short wait while (fifoCount < packetSize) fifoCount = mpu.getFIFOCount(); // read a packet from FIFO mpu.getFIFOBytes(fifoBuffer, packetSize); // track FIFO count here in case there is > 1 packet available // (this lets us immediately read more without waiting for an interrupt) fifoCount -= packetSize; mpu.dmpGetQuaternion(&q, fifoBuffer); mpu.dmpGetGravity(&gravity, &q); mpu.dmpGetYawPitchRoll(ypr, &q, &gravity); #if LOG_INPUT Serial.print("ypr\t"); Serial.print(ypr[0] * 180/M_PI); Serial.print("\t"); Serial.print(ypr[1] * 180/M_PI); Serial.print("\t"); Serial.println(ypr[2] * 180/M_PI); #endif input = ypr[1] * 180/M_PI + 180; } } void loopAt1Hz() { #if MANUAL_TUNING setPIDTuningValues(); #endif } void loopAt5Hz() { #if MOVE_BACK_FORTH moveBackForth(); #endif } //move back and forth void moveBackForth() { moveState++; if (moveState > 2) moveState = 0; if (moveState == 0) setpoint = originalSetpoint; else if (moveState == 1) setpoint = originalSetpoint - movingAngleOffset; else setpoint = originalSetpoint + movingAngleOffset; } //PID Tuning (3 potentiometers) #if MANUAL_TUNING void setPIDTuningValues() { readPIDTuningValues(); if (kp != prevKp || ki != prevKi || kd != prevKd) { #if LOG_PID_CONSTANTS Serial.print(kp); Serial.print(", "); Serial.print(ki); Serial.print(", "); Serial.println(kd); #endif pid.SetTunings(kp, ki, kd); prevKp = kp; prevKi = ki; prevKd = kd; } } void readPIDTuningValues() { int potKp = analogRead(A0); int potKi = analogRead(A1); int potKd = analogRead(A2); kp = map(potKp, 0, 1023, 0, 25000) / 100.0; //0 - 250 ki = map(potKi, 0, 1023, 0, 100000) / 100.0; //0 - 1000 kd = map(potKd, 0, 1023, 0, 500) / 100.0; //0 - 5 /* Serial.print(kp); Serial.print(", "); Serial.print(ki); Serial.print(", "); Serial.println(kd); */ } #endif |

